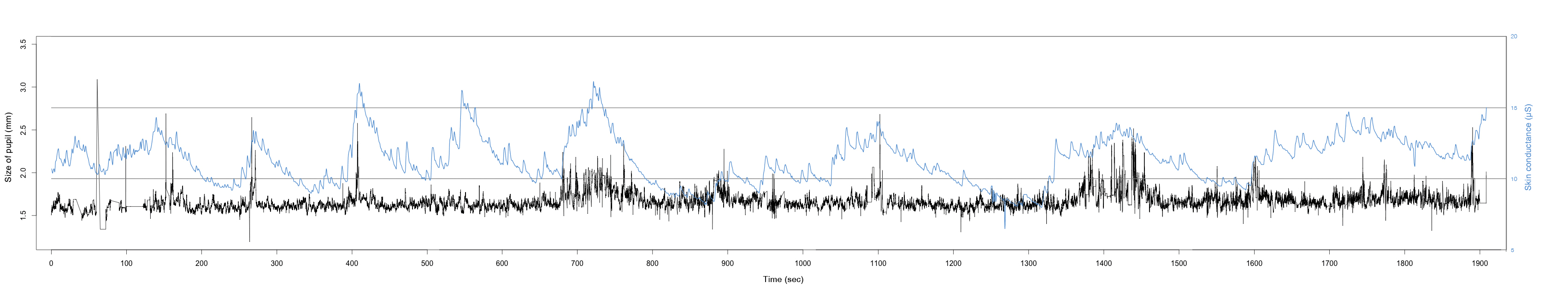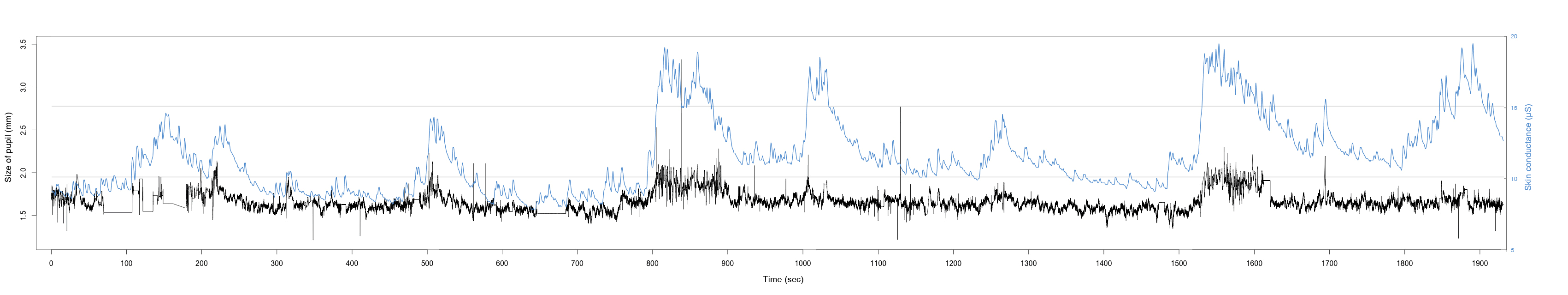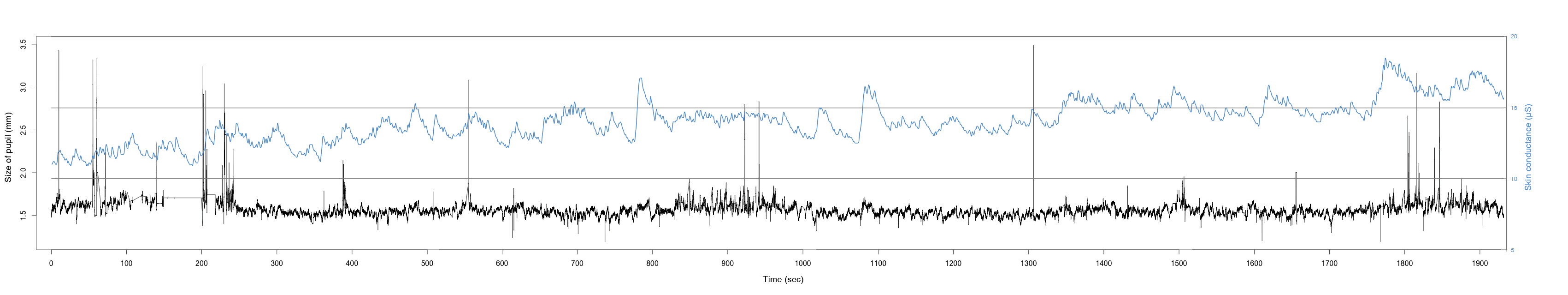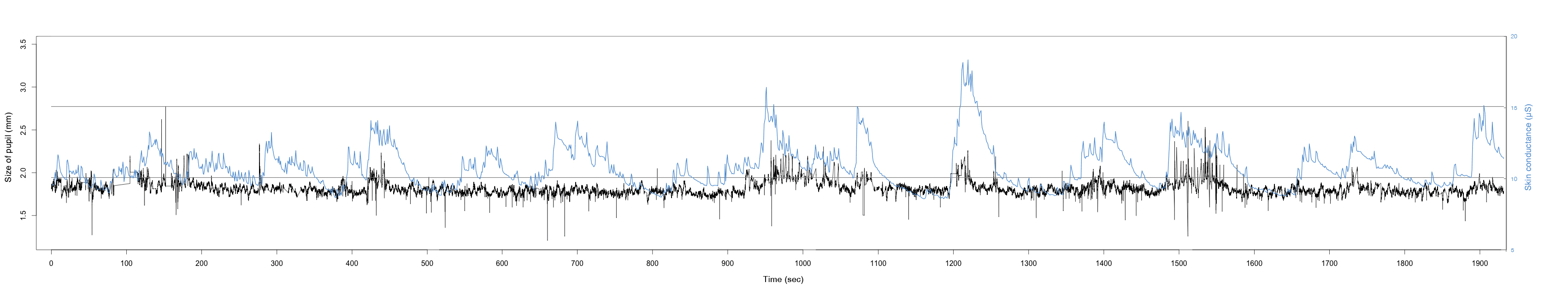
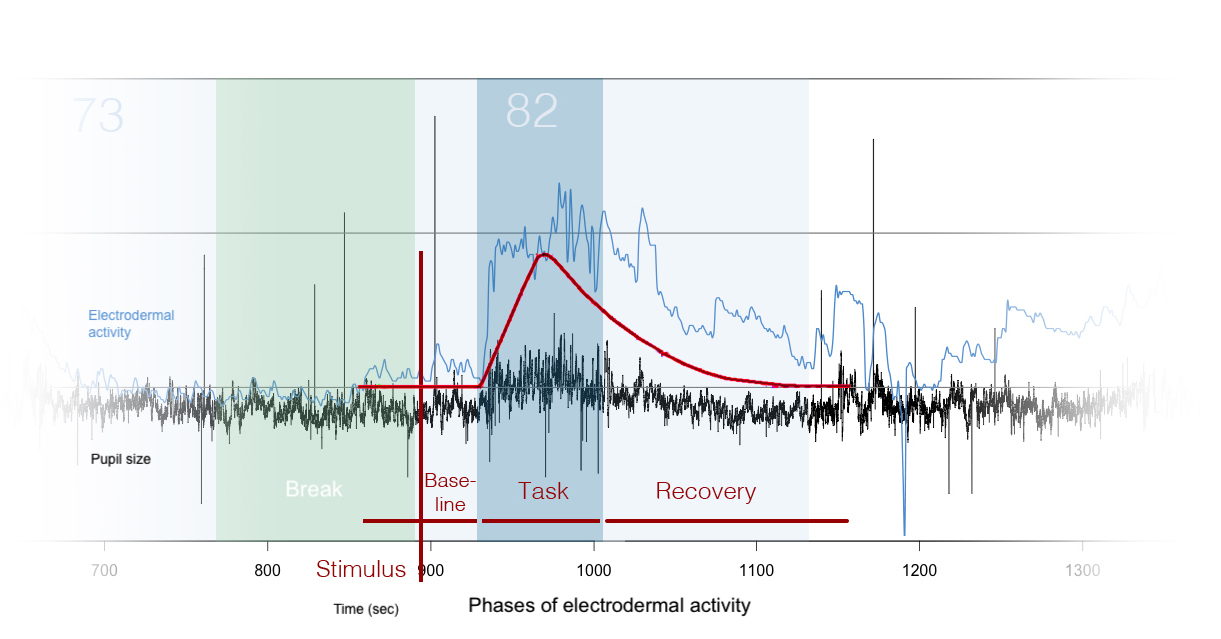
INTERRUPTIONS AFFECT STRESS AND PRODUCTIVITY
Interrupting work does not only increase stress but directly and indirectly decreases the productivity of the individual and thus the productivity of the company. Emails are a common interruption. The change of activity between email as a communication medium (secondary task) and a work-based application (primary task) describes a common working practice. Interruptions and their effect on the digital workplace are subject of this Masters Thesis. It shows whether design decisions such as autonomy are of significant relevance.